3.7. Transforming the data with your own code ¶
The additional method offered by OnTask to manipulate the data in a workflow table is to execute arbitrary Python code encapsulated as a Python module and placed in a predefined folder in the computer hosting the server. These Python modules are called either Transformations or Models and require some previous configuration by the system administrator, namely, the Python module must be installed in a specific folder.
The purpose of these transformations and models is to allow arbitrary processing of the data attached to a workflow such as machine learning algorithms, predictive models, etc. The list of transformations available for execution can be accessed through the links Run Transformation and Run Model in the Table button of the top menu. The modules available for execution are shown in a table like the one in the next figure.
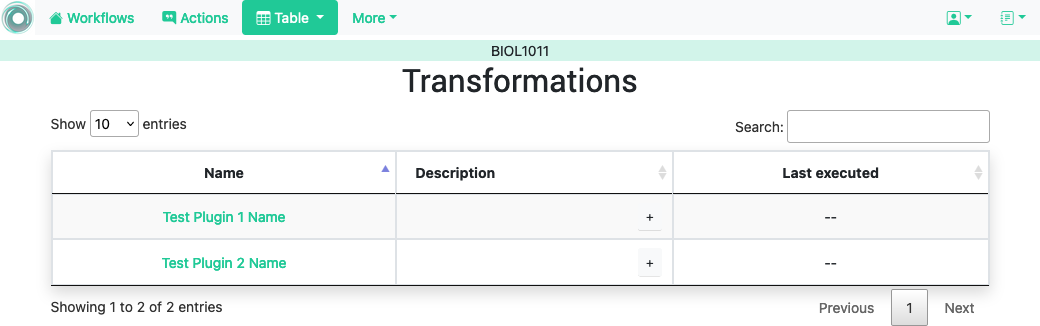
Each transformation is shown with a name, a description and the last time the code was modified (based on the file modification time). The link in the name opens a form to introduce the information required for execution. The following figure shows and example of this page.
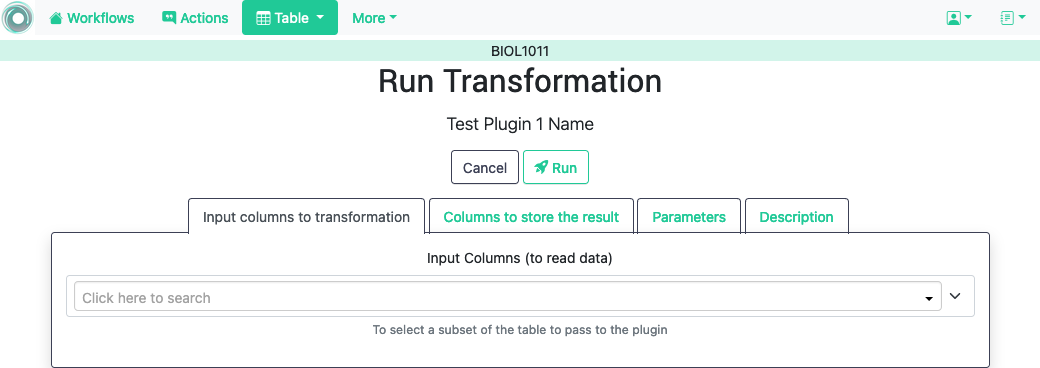
The information requested in this page is divided into the following tabs.
- Input columns to transformation
-
This field is to select the subset of columns from the data table that will be passed when invoking the transformation. It is possible for a transformation to define a set of fixed column names as inputs. If this is the case, the field in this tab shows those names and does not allow changes.
- Columns to store the result
-
The middle tab in this page includes fields to obtain the output column names (the transformation may supply suggestions, an optional suffix to add to the result column names to be able to differentiate between multiple executions of the transformation, and a key column to be use when merging the result of the transformation with the current table.
- Parameters
-
This tab contains a form to pairs (name, value) as defined by the transformation.
- Description
-
Text describing in detail the effect of the transformation.
Once the data is filled, the program is executed by clicking in the Run button. The execution is done in the background (it may take some tie), and a link to the log including the report is shown.
3.7.1. Transformation requirements ¶
The information in this section is for those users that want to write a Python module. The modules installed in the predefined folder need to satisfy several requirements to be considered for execution within OnTask. More precisely, each module must be stored in its own folder (as a Python module). The file
__init__.py
in the module must contain:
-
Module variable
class_namewith the name of the class in the file that contains the required definitions. -
The definition of a class with the name stored in the previous variable. The class must inherit either from
dataops.plugins.OnTaskTransformationordataops.plugins.OnTaskModel. -
Class field
namewith the transformation name to show to the users. -
Class field
description_txtwith a string with the detailed description of what the transformation does -
Class field
input_column_nameswith a potentially empty list of column names (strings). If the list is empty, the columns are selected by the user at execution time. -
Class field
output_column_nameswith a potentially empty list of names (strings) of the columns to be used for the output of the transformation. -
Class field
parameterswith an optionally empty list with tuples with the following structure:('name', type, [list of allowed values], initial value, help_text)These elements will be requested from the user before executing the transformation through a form. The conditions on these values are:
-
name must be a string
-
type must be a string equal to “integer”, “double”, “string”, “datetime” or “boolean”.
-
The list of values is to restrict the possible values
-
The initial value must be of the type specified by the second element.
-
Help_text a string to show as help text
-
-
Class method
runthat receives:-
a pandas data frame with the data to process
-
a string with the name of the key column that will be used to merge the result.
-
A dictionary of pairs (name, value) with the parameters described in the previous element.
an d returns a result Pandas data frame. This frame must have one column with the key column name provided so that it can be properly merged with the existing data.
-
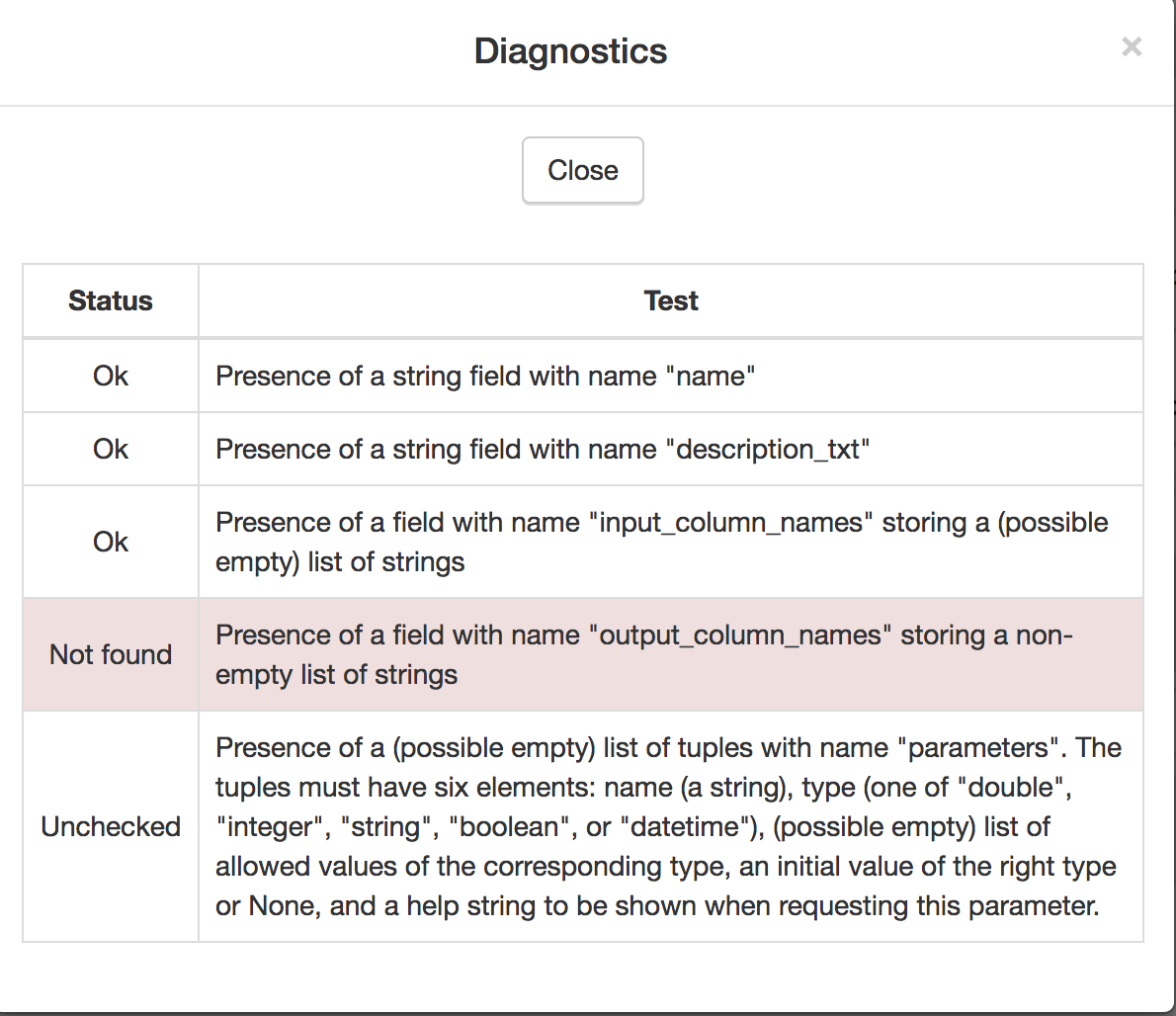
If a transformation does not comply with these properties the system administrator will see a summary of these checks to diagnose the problem.
See the section Write your own data processing code for an example of a module.